 Because injuries are never planned, be prepared by bookmarking Dr. Steven Chudik's online scheduling tool today!
Because injuries are never planned, be prepared by bookmarking Dr. Steven Chudik's online scheduling tool today!
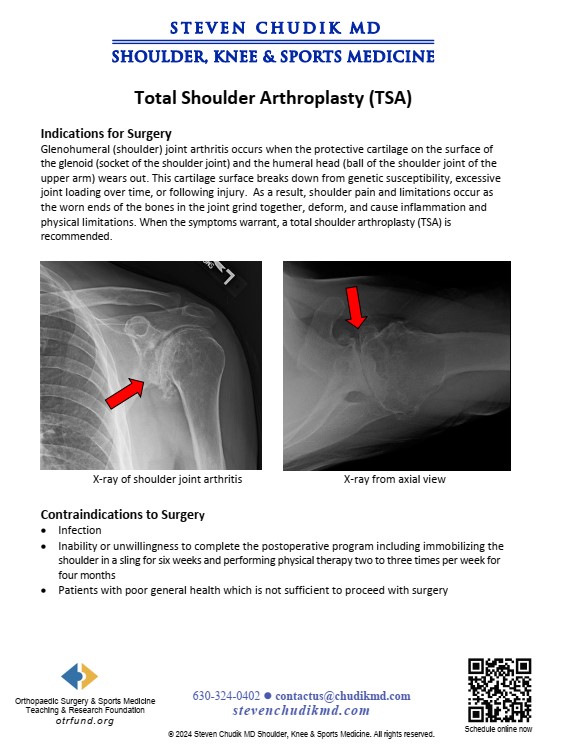
Indications for Surgery
Glenohumeral (shoulder) arthritis occurs when the protective cartilage covering the ends of the
bones at the shoulder joint wears out. The shoulder is comprised of the glenoid (socket of the
shoulder joint) and the humeral head (ball of the shoulder joint on the end of the upper arm
bone). The cartilage covering the glenoid and humeral head wears out from excessive joint
loading over time in patients genetically susceptible to arthritis or following injury. Shoulder
pain and limitations occur as the worn bony ends of the joint grind together and cause
mechanical symptoms and inflammation. When the symptoms warrant, a total shoulder
arthroplasty (TSA) is recommended.
Articular cartilage lesions and arthritis involving the glenohumeral joint can be difficult to treat. Conventional methods include arthroscopic debridement, abrasionplasty, microfracture, cartilage restoration procedures, resurfacing and replacement. Restoration, resurfacing, and replacement methods achieve limited access to the glenohumeral joint following subscapularis transection and dislocation. Click the link below to learn more…
Learn More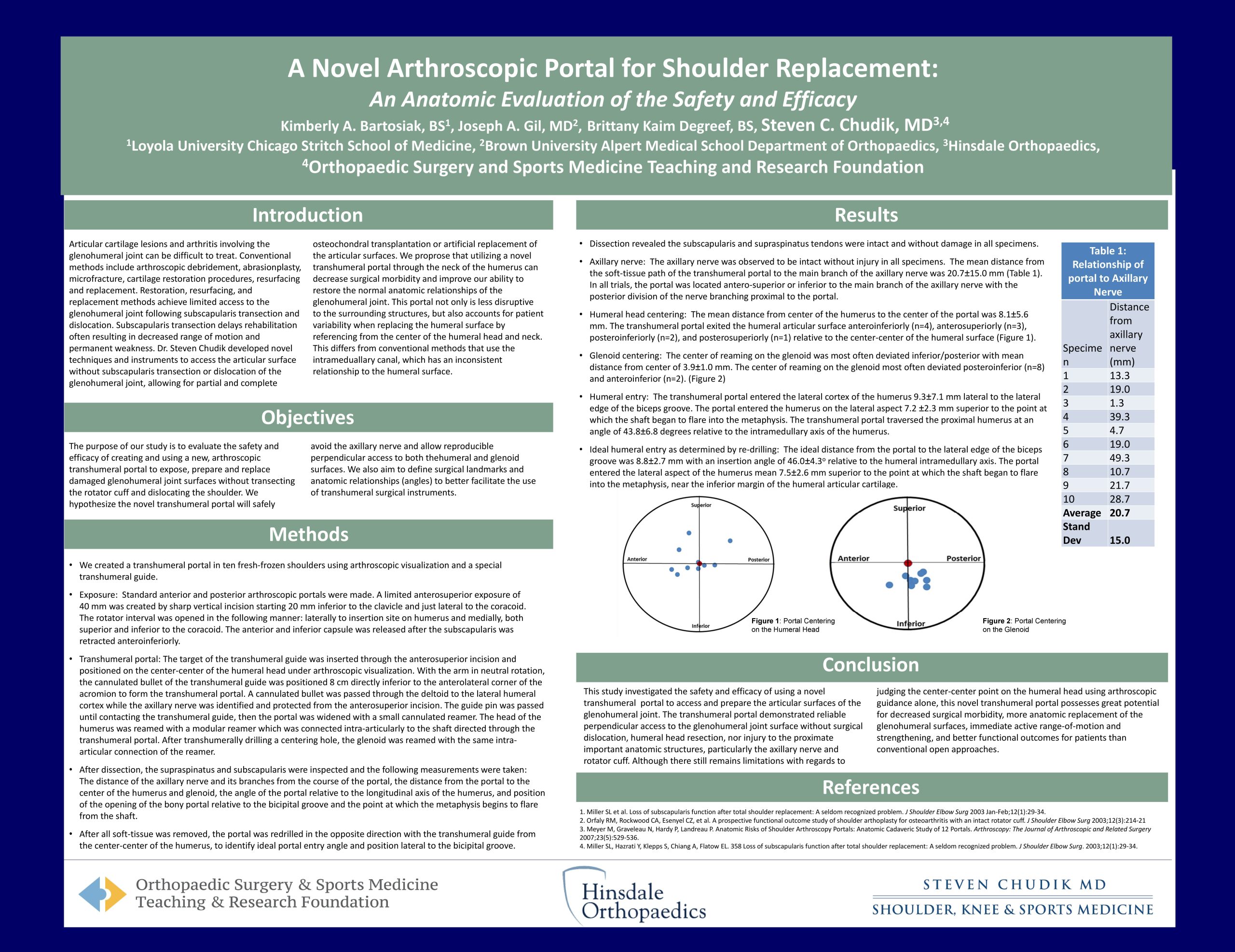
Total shoulder arthroplasty is a common surgical procedure indicated for arthritis of the glenohumeral joint. Although this surgical procedure is highly successful in restoring the function of the glenohumeral joint and relieving pain associated with glenohumeral degeneration, it is not free of post-operative complications. Click the link below to learn more…
Learn More
Content provided by Dr. Chudik not to be used for diagnosis and treatment. You can receive a proper evaluation and diagnosis by making an appointment with Dr. Chudik