Proper warm-up, conditioning exercises can help prevent youth sports injuries
Proper warm-up, conditioning exercises can help prevent youth sports injuries
Displaced fractures of the tuberosities which are separated often require surgery to re-position and fix the tuberosity bone fragments back in normal position to re-attach the associated rotator cuff muscles and restore normal shoulder function. Dr. Steven Chudik, orthopaedic shoulder surgeon developed a special arthroscopic procedure to repair the fragments which most commonly is performed through open surgery.
Click to Learn More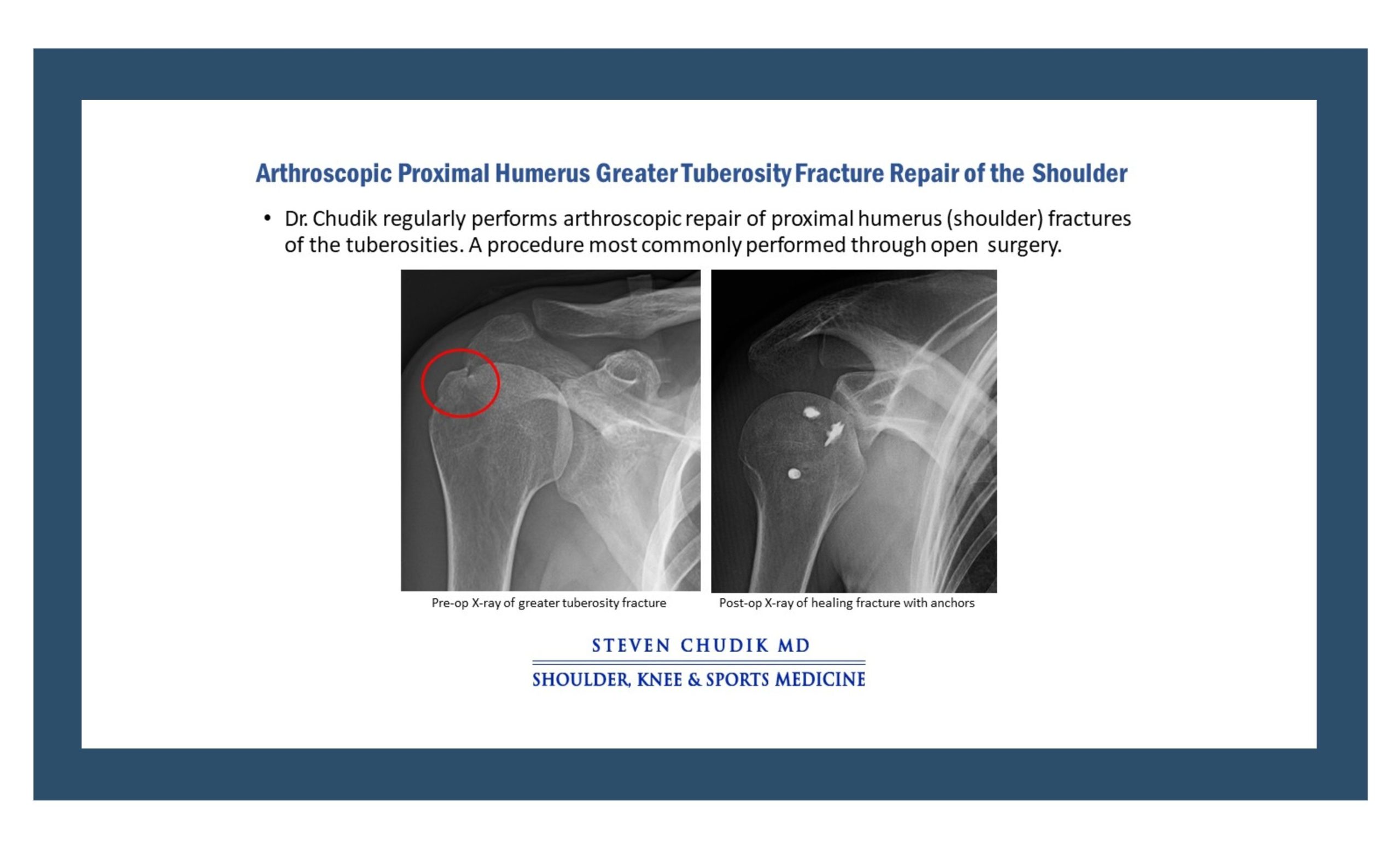
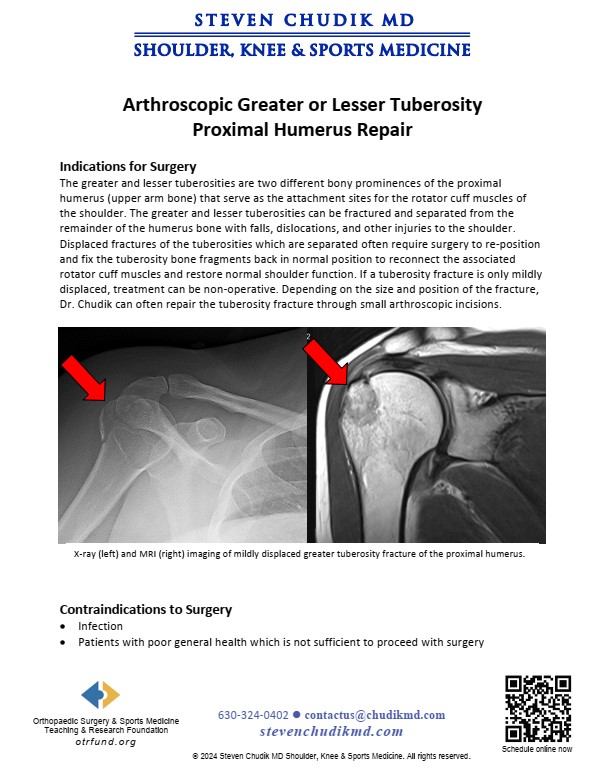
The greater and lesser tuberosities are two different bony prominences of the proximal humerus (upper arm bone) that serve as the attachment sites for the rotator cuff muscles of the shoulder. The greater or lesser tuberosities can be fractured and separated from the remainder of the humerus bone with falls, dislocations and other injuries to the shoulder. Displaced fractures of the tuberosities which are separated often require surgery to re-position and fix the tuberosity bone fragments back in normal position to re-attach the associated rotator cuff muscles and restore normal shoulder function. If a tuberosity fracture is only mildly displaced, treatment can be non-operative. Depending on the size and position of the fracture, Dr. Chudik often can repair the tuberosity fracture arthroscopically through small arthroscopic incisions. The surgery is generally performed as an outpatient surgery (you go home the same day).
Following surgery, your shoulder will be placed in a sling for approximately six weeks while the bone heals. Physical therapy often is needed to mobilize the shoulder, regain range of motion, strength and function. You may return to unlimited activities when there is no pain and full shoulder range of motion, muscle strength and endurance, and functional use has been restored. This usually requires four to six months following a repair of a tuberosity fracture.
Learn More